Note
Click here to download the full example code
Smokes-Friends-Cancer¶
The smokes-friends-cancer example is a common first example in probabilistic relational models, here
we use this set to learn a Relational Dependency Network (srlearn.rdn.BoostedRDN).
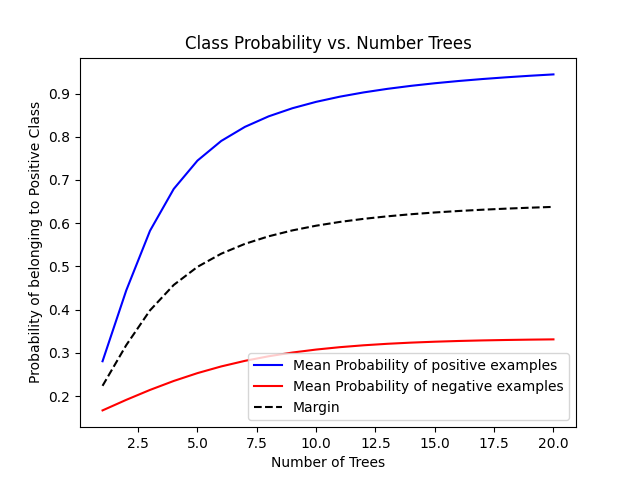
This shows how the margin between positive and negative examples is maximized as the number of iterations of boosting increases.
Out:
/home/docs/checkouts/readthedocs.org/user_builds/srlearn/checkouts/stable/srlearn/base.py:70: FutureWarning: solver='BoostSRL' will default to solver='SRLBoost' in 0.6.0, pass one or the other as an argument to suppress this warning.
", pass one or the other as an argument to suppress this warning.", FutureWarning)
<matplotlib.legend.Legend object at 0x7f040d75e750>
from srlearn.rdn import BoostedRDNClassifier
from srlearn import Background
from srlearn.datasets import load_toy_cancer
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
train, test = load_toy_cancer()
bk = Background(modes=train.modes)
clf = BoostedRDNClassifier(
background=bk,
target="cancer",
max_tree_depth=2,
node_size=2,
n_estimators=20,
)
clf.fit(train)
x = np.arange(1, 21)
y_pos = []
y_neg = []
thresholds = []
for n_trees in x:
clf.n_estimators = n_trees
probs = clf.predict_proba(test)
thresholds.append(clf.threshold_)
y_pos.append(np.mean(probs[np.nonzero(clf.classes_)]))
y_neg.append(np.mean(probs[clf.classes_ == 0]))
thresholds = np.array(thresholds)
y_pos = np.array(y_pos)
y_neg = np.array(y_neg)
plt.plot(x, y_pos, "b-", label="Mean Probability of positive examples")
plt.plot(x, y_neg, "r-", label="Mean Probability of negative examples")
plt.plot(x, thresholds, "k--", label="Margin")
plt.title("Class Probability vs. Number Trees")
plt.xlabel("Number of Trees")
plt.ylabel("Probability of belonging to Positive Class")
plt.legend(loc="best")
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 13.920 seconds)